
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JtahmxKjfKs
7 Surprising Magnesium Benefits You Don't Know

Magnesium is a fascinating mineral .
It's involved in over 350 different enzymes in the body , and we may find that it's involved in a lot more .
But what's interesting about enzymes is that they speed up the chemical reactions in the body of a factor of like a 100000000 times faster than if you didn't have that enzyme .
There's definitely things that you know .
It helps with heart disease .
It helps with cramping at night .
If you have those cramps in your calves , it helps you sleep .
It's involved in helping you reduce anxiety .
It makes you more relaxed .
It actually makes your arteries less stiff .
And that's going to help you lower blood pressure .
You probably also know that magnesium works with calcium is kind of like a teeter totter effect .
The more calcium you have , the less magnesium you're going to have , and vice versa .
So you need calcium and magnesium in the right ratios , especially involved in the muscle contraction and relaxation .

So where calcium tends to be involved in contraction , magnesium is all about relaxation .
And this is why you have all sorts of muscle problems if you have a deficiency in magnesium , like a cramp , like , twitching , like tetany .
A lot of times people take magnesium because they have headaches .
So magnesium is good for headaches .
And so if there's any problem involving with the nerve and muscle , irritation or even arrhythmias in the heart , think magnesium .
But let's talk about the things that you probably have never heard about that are quite interesting .
There's an enzyme that helps you regulate cholesterol .
It's called HMG CoA Reductase .
This is the enzyme that statins work on , and it just so happens that magnesium parallels the effects of statin .

So it can help you regulate LDL or an increased HDL , and help you regulate your triglycerides as well .
Magnesium is also involved in enzymes related to lecithin , which is like the antidote to cholesterol .
And so without magnesium , you're gonna have a lot of issues with cholesterol and the ratios , as well as having lecithin work .
Now the other big thing that magnesium is involved with is making ATP .
That is the energy currency of the body , and without that , you just can't make energy .
So this is why magnesium is the 2nd most needed mineral in the body just behind potassium .
So without magnesium , you could be tired all the time .
Now the other thing about magnesium is that it can help you lower adrenaline , cortisol , and something called ACTH .

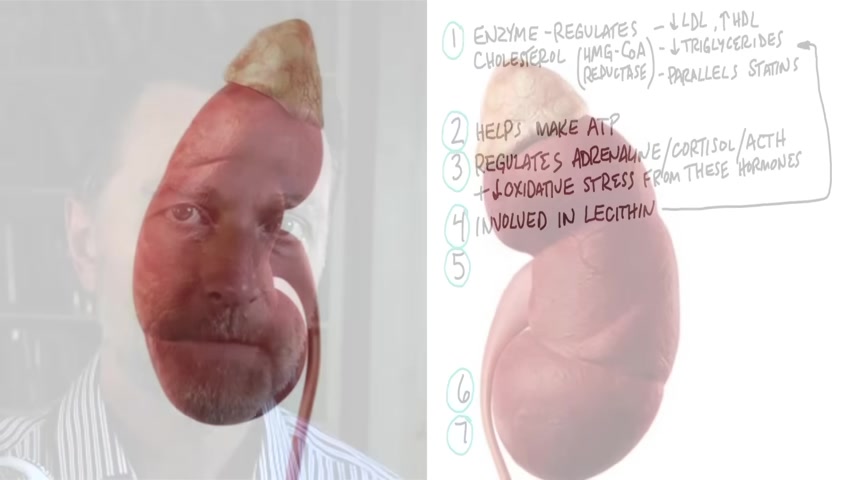
ACTH is this , hormone that is released from the pituitary that tells the adrenals to release cortisol .
And so if you have less regulation on that hormone , you're gonna have higher levels of stress .
And this is why magnesium is really good for stress and anxiety because it helps to normalize this ACTH , cortisol , and adrenaline , as well as help to counter all the oxidative stress that comes with these stress hormones .
So magnesium is very protective at the cellular level .
Magnesium is a natural calcium channel blocker because it opposes calcium , which means it's really good for blood pressure .
But , typically , they don't know why .
Well , the reason is this .
It can act like a natural calcium channel blocker .
Calcium channel blockers are a common medication for hypertension .

Well , magnesium is a natural version of that with virtually no side effects , but it also can act at the same time as a beta blocker .
So with one angle , it helps balance calcium , and from another angle , the beta blocker that has to do with reducing stress in the arteries and that whole system .
Now a couple other really cool things that magnesium is involved with .
Number 1 , it's in natural antithrombotic .
Basically , it's a natural blood thinner .
Another thing you may not know about magnesium is that it can help you lower your blood sugars .
It is really important in kind of undoing insulin resistance .
And the last thing , which is actually probably the most important function of magnesium , magnesium is involved in making DNA without having the perfect blueprints that can create a huge chain reaction .

And And we typically need about 310 to about 420 milligrams of magnesium every day , and not a lot of people get that .
And so they're gonna be deficient , and they're gonna have these problems .
Magnesium is at the heart of chlorophyll .
So anything green , like dark leafy green vegetables , and this is something that a lot of people don't consume .
But then you also have nuts and pumpkin seeds , dark chocolate , of course , without the sugar , sea kelp , and even certain types of sea salt that are low sodium type sea salt .
But we also have to look at those things that are depleting our magnesium .
Okay ?
Refined sugars , refined carbohydrates , alcohol , diuretics , diarrhea , having a low stomach acid , and even having certain type of gene variations .
That can also be a problem .
It's actually quite common where people just don't seem to absorb magnesium like they should .


And And for those people , it's even more important to stay away from alcohol and things that deplete your magnesium , and and even probably supplement with a good form of magnesium .
And the type of magnesium I would recommend is magnesium glycinate , which is very bioavailable .
Now since we're on this interesting topic of magnesium , if you haven't seen my other video on magnesium , I put it up right here .
Check it out .
Are you looking for a way to reach a wider audience and get more views on your videos?
Our innovative video to text transcribing service can help you do just that.
We provide accurate transcriptions of your videos along with visual content that will help you attract new viewers and keep them engaged. Plus, our data analytics and ad campaign tools can help you monetize your content and maximize your revenue.
Let's partner up and take your video content to the next level!
Contact us today to learn more.