
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D2UEHG6lx4A
Magnesium Protects Against the Bad Effects of Calcium

We're gonna talk about magnesium's effect on calcium .
But let's first talk about what magnesium does .
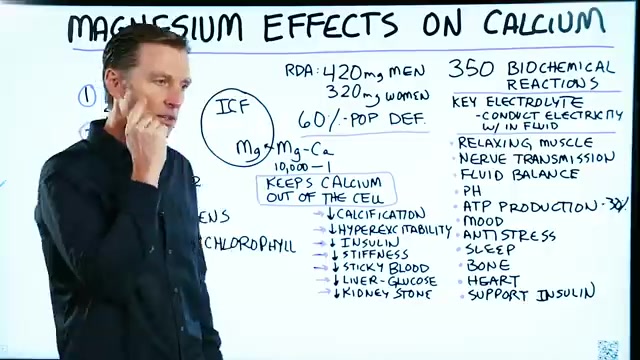
It's involved in over 350 biochemical reactions .
It's a coenzyme , and that means it's a helper mineral involved in enzyme reactions which are it's like the protein machines in the body that do all the work .
Magnesium is also a key electrolyte .
Electrolytes conduct electricity within the fluid of your body .
Magnesium , affects the relaxation of muscle , nerve transmission , fluid balance , pH , ATP production which is the energy currency of the body .
Magnesium is also involved in mood , making serotonin .
It's also involved in making melatonin which actually can help you sleep as well .
It's an anti stress mineral involved in the adrenal hormones .

It's involved in bone physiology , heart physiology and supporting insulin .
So you can see it's very very important .
Now up to 60% of the entire population has a subclinical magnesium deficiency .
And subclinical meaning that it doesn't show up in a blood test but you're deficient because the actual deficiency is inside the cell .
98% of all the magnesium is inside the cell not outside the cell .
So when you get a blood test and you find that your magnesium levels are normal in your blood , it doesn't really mean anything because most of the magnesium is inside the cell .
The RDA's for magnesium in men are 420 milligrams and for women , they're 320 .
The best sources of magnesium are in pumpkin seeds and then spinach , and then Swiss chard , and sunflower seeds , leafy greens , and salmon .
Chlorophyll , which is the blood the plant has a very similar chemistry to our own blood .

And the difference is that we have iron , which is red in the center of our blood molecule , and the plant has , magnesium which is a slight green color in its , chlorophyll .
One of the really important things about magnesium is keeping calcium outside the cell .
If there's enough magnesium inside the cell , it can prevent calcium from going inside the cell and creating damage .
In fact , the ratio of magnesium to calcium inside the cell is 10000 to 1 .
When there's low magnesium and the calcium gets out of control , you start getting calcification .
But if you think about it , how many medical conditions involve calcification ?
Calcification in the arteries , calcification in your kidneys , calcification in your eyes , on the nerves , in the brain .
There are many many conditions that involve excessive amounts of calcium build up .
And yes , we need vitamin k 2 to actually help mobilize the calcium out of the soft tissue .

Magnesium is just as important .
When we have too much calcium and too little magnesium , you get a hyperexcitability of the nervous system .
So you start getting little twitches , you know , in different parts of your body .
Maybe the left eyelid or another part of the body .
You also have problems with insulin .
Insulin starts going up .
So having the right ratios of magnesium to calcium can keep your insulin in check .
Also , having enough magnesium can prevent calcium from causing stiffness and sticky blood which can lead to excess clotting .
Also , having enough magnesium actually prevents the liver from producing too much glucose .
And lastly , I already mentioned this , having enough magnesium can prevent the formation of kidney stones .
So I recently created several really interesting videos about magnesium .
One was , the relationship between magnesium and your sleep cycles and the other is the best foods , that are magnesium rich and keto friendly .

I put them right on the screen and also down below .
Check them out .
Are you looking for a way to reach a wider audience and get more views on your videos?
Our innovative video to text transcribing service can help you do just that.
We provide accurate transcriptions of your videos along with visual content that will help you attract new viewers and keep them engaged. Plus, our data analytics and ad campaign tools can help you monetize your content and maximize your revenue.
Let's partner up and take your video content to the next level!
Contact us today to learn more.