
https://youtu.be/CiN5pD1kR3g?si=7T3sPmzaGgAyJM94
How Much Dietary Proteins Will Prevent Muscle Loss Need of Protein & Loss of Muscle – Dr.Berg
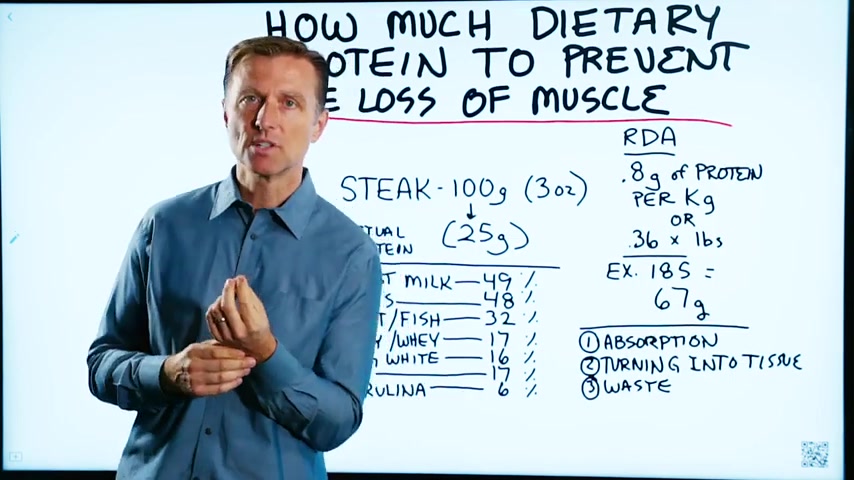
So I wanted to do this , video on protein because it's a common confusion with so many people .
We're gonna answer the question , how much dietary protein do you need to consume to prevent the loss of muscle ?
But let me just talk about 1 piece of this problem at a time .
Okay .
The RDAs .
The , recommended dietary allowance for protein is point 8 grams of protein per kilogram in weight .
Okay now I'm from the US so we don't use kilogram , we don't use grams as much , we use pounds .
So if you're from other parts of the world this would make sense to you .
But if you're from the US , this is gonna make more sense , this formula which is basically 0.36 times your pounds .
Okay .
So I weigh a £185 .
So I would times point 36 times 185 and that comes out to 67 grams of protein per day .

That's how much I'm supposed to consume .
Okay .
There's many problems with this recommendation , which I'll get into .
But that's , the minimum amount that I would need .
Now if we just take a steak for example .
Okay ?
A 100 grams of steak , which is a little over 3 ounces .
Let's just say it's 3 ounces to make it simple .
Realize that this 100 gram weight of steak only gives us 25 grams of actual protein because most of it is water .
Now this might be shocking to you .
You're only getting a small portion of that being protein .
And now if we take it 1 step further , and I'm not gonna even talk about the absorption of the protein , I'll talk about that in the next slide , but I'm talking about how much of this protein actually turns into muscle or body tissue ?
This is number 2 , turning into body tissue .
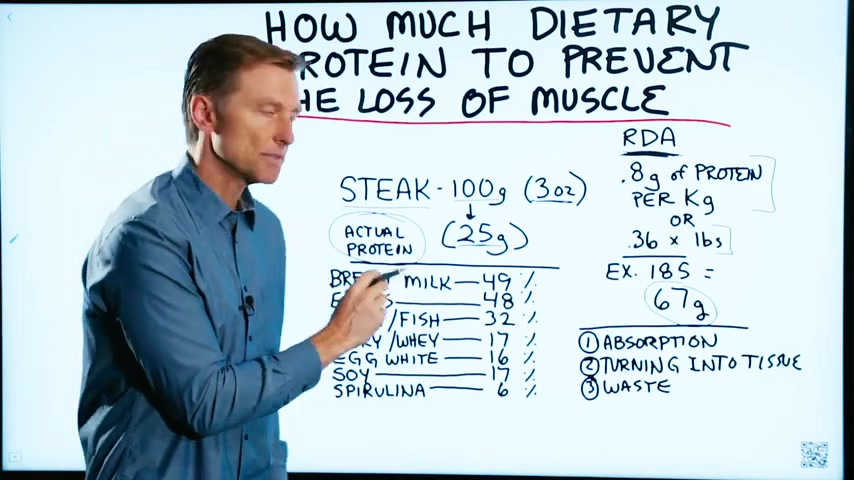
Well , let's take a look at the type of protein first .
We've got breast milk , which actually 49% of breast milk turns into body tissue .
Eggs , 48% .
That means 52% of those eggs do not turn into body tissue .
They're either used as fuel or is just wasted , okay , through the urine .
And eggs are at the top of the list because we really can't get access to breast milk .
Alright .
So now we have meat , fish , poultry , 32% .
Okay .
So that's even lower .
So you could imagine how much waste is occurring when you consume meat and fish .
So if we take 25 grams , okay , and then we take 32% of that , which comes out to , roughly a little more than 7 grams .
Okay .


So now we're getting with the actual amount of protein that's turning in the body tissue .
7 grams .
So the RDAs are very confusing because are they talking about actual absorption ?
Or are they talking about turning in the body tissue ?
It's almost impossible to find this information .
I have not found it .
Okay .
All I know is that out of the steak , you're only getting like 7 grams .
K .
Which is a very small amount .
Now you might be thinking , well , I'll just eat more protein .
Yes .
Okay .
You could do that .
But realize , with that extra protein comes more waste and comes more product as fuel .
Okay .
So it can turn into sugar , so you have that aspect .
I'm not saying it's going to be a big problem for blood sugars , but I'm just saying that , you're not getting as much as you think turning into body tissue .
Then when we get into dairy , like cheese or whey , you're only getting 17% of that turning in the body tissue .
It's even less .
Egg whites without the yolk .
Look at that .
That's actually 16% .

So it just goes to show you how important it is to consume protein in its whole form with fat .
You do not want to consume lean protein , as in whey .
You want to do natural the whole package , the fat and the protein at the same time .
Look at soy , 17% .
So the egg whites and soy are very low on the list .
So you could imagine if this was , soy and you'd take 17% of that , so it's just a fraction .
Spirulina is only 6% , not very much .
Now in a recent video I did , I talked about actually taking essential amino acids in addition to your own protein .
And the reason I like that is that it can give you a 99% effect on turning into body tissue with only a 1% waste .
So presently , I'm doing that to enhance my protein amounts .
Okay .
So let's look at the next slide .
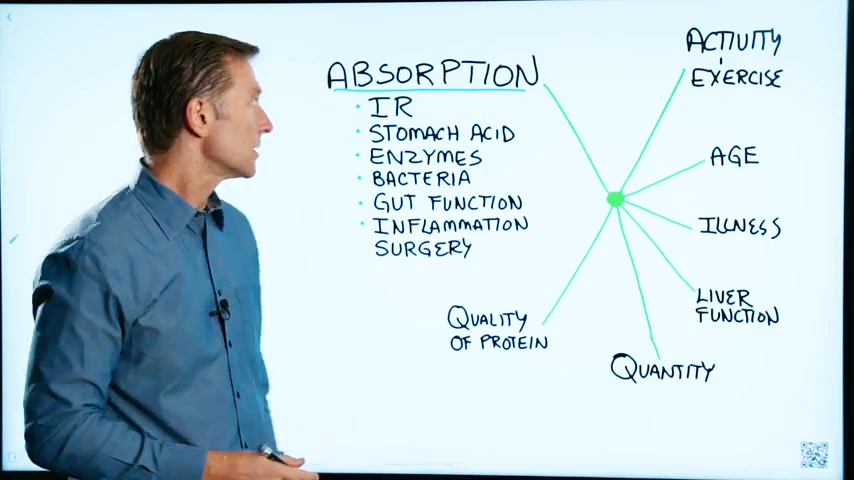
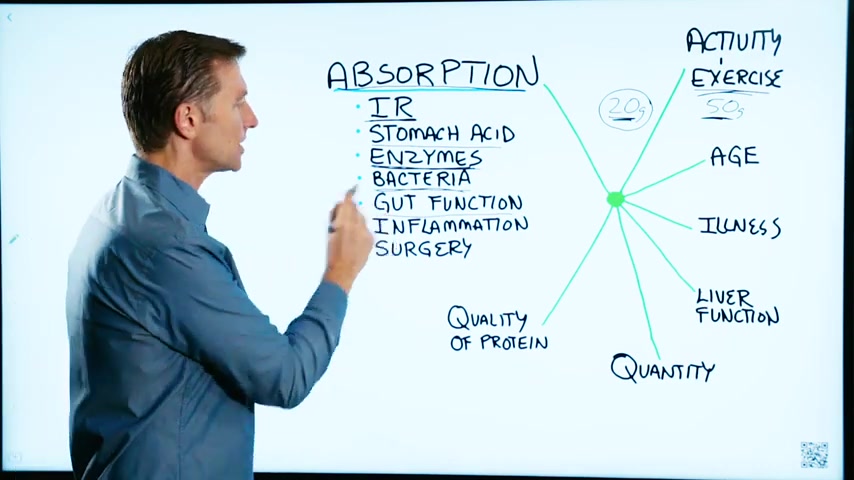
This has to do with the other variables , that influence your proteins .
Number 1 , absorption .
This is why it's very difficult to determine how much protein an average person needs .
I'm gonna give you some ideas in a bit , but let's first talk about some of the other barriers you're gonna run into .
Number 1 , insulin resistance .
Most people have a problem with this .
They're not able to absorb the amino acids because they they have insulin resistance .
But as you start getting on keto and intermittent fasting , that improves so you're absorbing more amino acids .
Now the other problem with that is that you're not consuming as much carbohydrates , which means your insulin is also going lower .
It's becoming more effective , but it's going lower .
And insulin is an anabolic hormone .
So it actually helps you make protein .

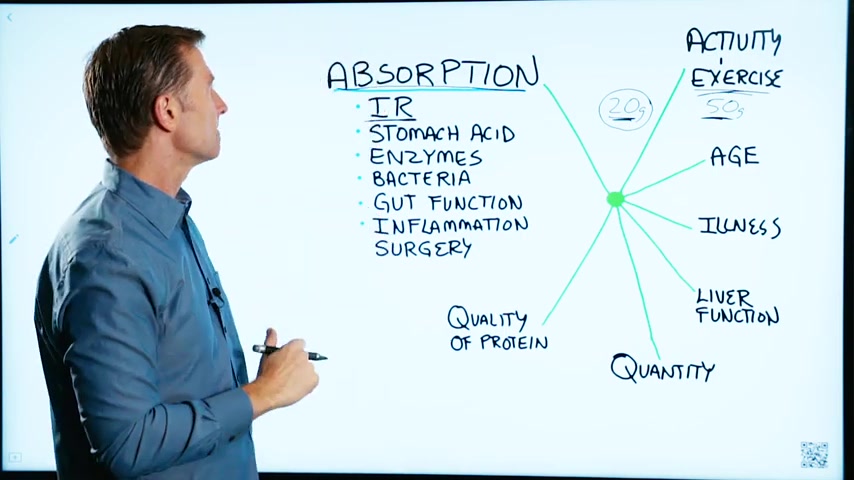
So with some people , especially if they're exercising , we may wanna keep their carbs at 50 grams instead of 20 .
Okay ?
Which will actually give them a little more insulin to keep up with the activity .
But people that are not exercising would do much better at a smaller amount , let's say 20 grams .
Because first of all they're not gonna need as much protein .
And if we keep the carbs low , they'll do fine with the small amount of insulin .
So it really there's just a lot of things going on here .
So we have insulin resistance , we have the amount of stomach acid that a person has .
Most , everyone over the age of 50 , especially when they get to 60 , 70 , 80 , they start losing their stomach acid .
Now they can't even break down the protein at the stomach level .
So they're gonna nearly always be protein deficient .
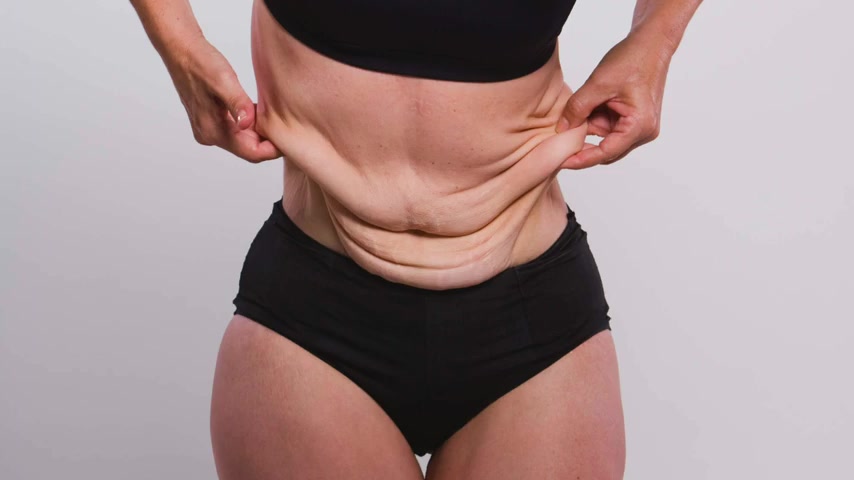

And it shows up in the loss of collagen , poor , joint function , fatigue , and sagging skin .
Now , if the person has a problem with their pancreas , let's say they're diabetic and their pancreas is exhausted because the pancreas makes insulin and other hormones , but it also makes enzymes .
So if the pancreas is exhausted , you're not gonna produce the enzymes to break down , protein as well .
So the combination of the enzymes in the stomach and the acid and then the enzymes in the pancreas all help in the breakdown of protein .
So this could be a deficiency just with that .
This is why a lot of people do better when they take enzymes .
Okay .
Bacteria .
Let's say your friendly bacteria is not there because you took antibiotics or you've eaten a lot of GMO foods , which destroy the microbes .
That alone can interfere with your absorption of protein right there .
And by the way , bacteria help you make , amino acids and proteins .
Okay .
Gut function .
So if you had gastric bypass or you had some surgery , that's gonna greatly influence your ability to absorb protein too .
If you had celiac where your little absorptive villi are now gone , you're not gonna absorb protein or nutrients as much .
So the gut function is very important .
If you have inflammation in your gut , that's also gonna stop the absorption of protein .
Okay .
So then we have , of course surgery .
I just mentioned that with the gastric bypass .
Or let's say you had some surgery in your colon .
That's going to influence your absorption .
Then we have the quality of protein .
Okay .
I'm talking about this right here .
These the type of protein and , of course , the grass fed or the organic .
So the quality of protein is very , very important .

And then the quantity of protein , like how much is too much .
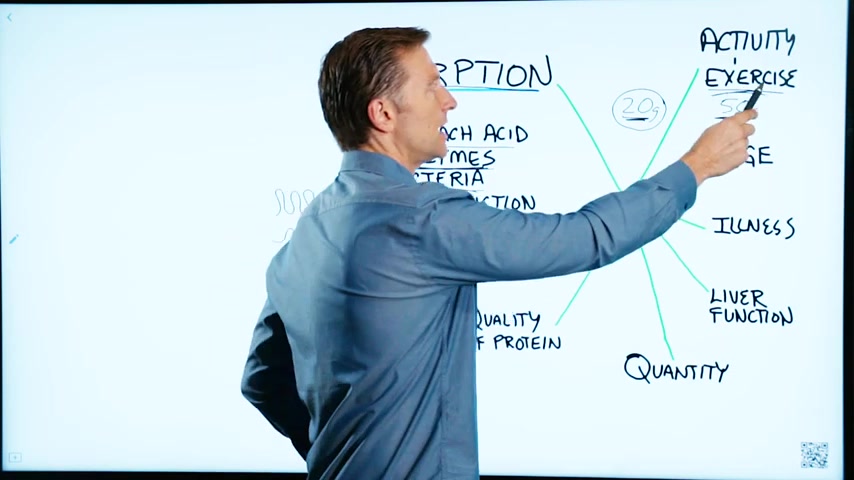
And then you get the exercise .
The more you exercise , the more protein you're gonna need .
K ?
So you need a little bit more if you if you're an athlete .
And then your age .
As you age , you lose your stomach acid .
So you do need a little more protein to compensate for all the things that are going on as you age .
And I think , a lot of people as they get older are protein deficient .
And they would greatly benefit from an amino acid product because these amino acids are already broken down .
They're not in the protein form so they're very easy to absorb .
Okay .
Illness .
Alright .
The if you have some type of chronic , degenerative disease or illness , you're gonna need more amino acids .
So this could increase the requirement as well .
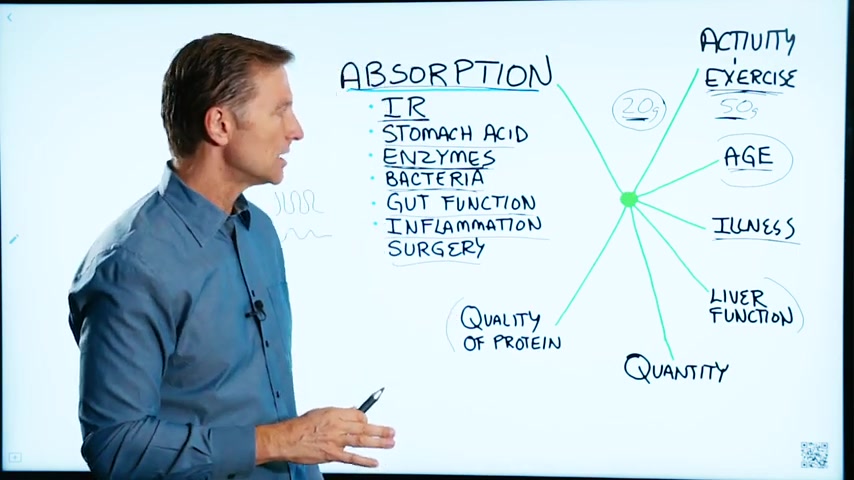
Also the liver function , if you have a fatty liver , cirrhosis , hepatitis , all of those conditions are going to inhibit your ability to absorb protein .
So the more damage you have in the liver and the kidney is going to increase the need .
The problem is the more protein you consume , the more waste you're gonna have .
And if your kidneys or liver are damaged , you're going to overload the body with too much waste .
So it's kind of a catch 22 .
That would be a good example of taking an amino acid product to supplement , with .
So now the question is what quantity , should you consume ?
Okay .
So I recommend instead of 0.8 you do 0.9 or 1.0 or maybe even 1.1 grams of protein per kilogram of weight .

That way at least you're gonna cover some of these other problems that might come up .
And also , if you keep the quality of protein high , the need of protein won't be as high .
Alright .
Hope that didn't confuse you even more .
Stay tuned for some more videos on this because there's a lot more to talk about .
But thanks for watching .
Oh , 1 last thing , because someone's going to ask this .
What you can do if you're not sure about kilograms , is you take your weight , okay , in pounds .
Okay .
So I'm 185 .
And you divide by 2.2 to get the kilograms .
Okay .
So you take the kilograms and then you times 1.0 , This is the amount of , protein you're gonna need times 1.0 to get the amount of protein that you need in grams .
Okay ?


So just take your weight , divide it by 2.2 to get your kilograms .
So now you can multiply it times , the amount of protein .
Oh , now this could be , point 9 or , you know , 1.1 .
But I would just to make it easy you can start right here .
And then comes the question , how do you really know you're getting the right amount of protein ?
You're gonna have to test it out .
You're gonna have to eat a little bit more or a little less and see how you feel .
How do your joints feel ?
How does your energy feel ?
That's probably gonna be the best thing .
Alright .
Now we're officially done with the video .
Are you looking for a way to reach a wider audience and get more views on your videos?
Our innovative video to text transcribing service can help you do just that.
We provide accurate transcriptions of your videos along with visual content that will help you attract new viewers and keep them engaged. Plus, our data analytics and ad campaign tools can help you monetize your content and maximize your revenue.
Let's partner up and take your video content to the next level!
Contact us today to learn more.