https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IVquJh3DXUA
Introduction to Linux and Basic Linux Commands for Beginners
Hello and welcome to Soy Tech in today's video .
I will give you guys a quick introduction to Linux and I'm going to show you how to use some very useful introductory Linux commands using a terminal window .
Now , just to be clear , this is a course for beginners who want to learn how to use commands on a Linux terminal .
Now , for those of you guys who are not familiar with Linux at all , let's give you a quick perspective .
Linux is not UNIX .
UNIX was created by a bunch of at and T employees in 1969 .
Linux was written by a name by a guy named Linus Trod who created the entire thing by himself and released it around 1991 .
Now , Linux is a powerful operating system , but it is especially designed for server systems and 90% of the world's fastest computers like supercomputers run on some form of Linux .
And this is because it's a rock solid system .
OK ?
So that was a quick history on Linux that was just to give you a perspective .
Now , Linux and UNIX are different .
Just remember that .
Now , one more thing before we dive in Linux comes in many different varieties which are called diss or distributions .
In this tutorial , we will use the popular U Bantu distribution of Linux , but there are others out there as well such as Fedora Mint and Debian and more even Android is a Linux distribution .
So the basic commands , we will , we will be running and learning today can be generally used on almost all different Linux distributions .
All right .
So let me go ahead and launch Linux .
And I just want to let you know I'm running Linux on my windows .
So what you do is you install virtual box , which is right here .
So let me launch that and inside a virtual box , you can install any operating system possible .
So I have put Utu Linux inside a virtual box on my Windows seven machine .
OK ?
So let me run this up .
And I just want to let you know , you can actually find a link in the description below which tells you how to uh install virtual box and Linux on , on your Windows seven if you want to go ahead and do that .
But this is the Utu Linux that is launching right now .
OK ?
So here you're looking at ubuntu Linux .
And uh before we dive into the commands , I'm gonna show you something real quick what you're seeing here , all these icons , all this desktop , all these nice graphical features .
This is called the G U I .
This is called the graphical user interface .
Now we are not worried about that today .
What we're worried worried about is the cli which is called the command line interface .
So you have to launch a terminal to go into the command line interface .
And then once you um search for an app , you can type in terminal which brings up the terminal right here and then you can actually click that and that is the terminal we will be working with .
All right .
So the first command we will be looking at today is the P W D command .
Oops , that's not typing .
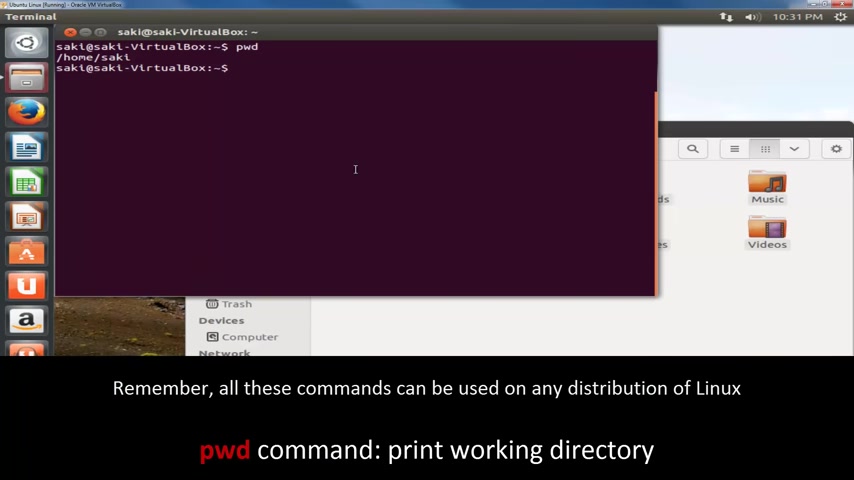
OK , P W D command , P W D D command stands for print working directory .
So when I press enter , it actually tells me which directory I am currently located at .
So if I go to my uh folder browser , um I am actually in home .
So which is right here .
So I'm looking at all these guys on my command prompt .
Now , the second command I wanna show you guys is the L S command .
When you press L S , it gives you a listing of everything which is in the current directory .
So the current directory is the directory , which is my user name and we're under home inside of home .
I've got all these guys .
So I've got the desktop downloads , music , public videos .
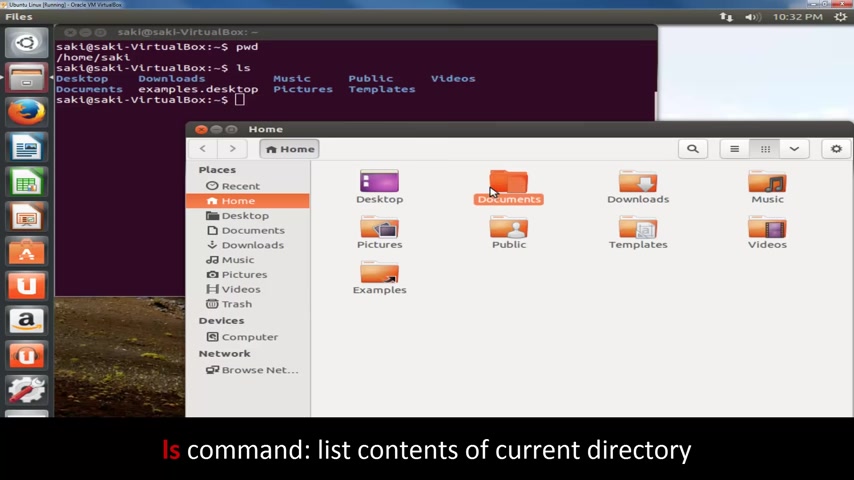
And if you come over here , that's all the same stuff you're going to see in a regular file explorer .
So here's a desktop documents downloads , music , same stuff that you see here .
So that is the L S command .
It's , it's , it , it stands for list and when you list it lists whatever is inside of your current directory .
Again , P W D stands for print working directory .
So it tells you where you are currently located in .
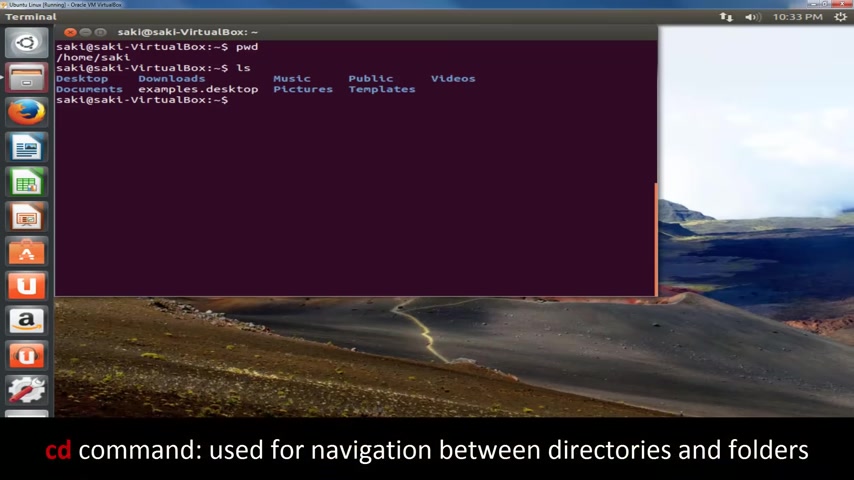
Now , as you can see when you have a pretty graphical user interface , you can see everything right in front of you .
But if you have a command line interface like this on a terminal , you're not going to be able to see anything .
So if I clear this , that's all you see .
So you have no idea where you are .
OK ?
So to see where you are P W D to see what you have at where you are , you type in list .
Now , the next command I'm gonna show you is called the CD command and CD command has a lot of variations .
CD is used for navigation .
So let's say I want to go to the uh downloads folder .
How do I go there ?
I type in CD and I type in downloads the name of the folder and just remember everything has to be exactly as it appears .
So the , the , the in , in Linux everything is case sensitive .
So this cannot be a uh um a small D , it has to be capitalized just like it is here .
OK ?
So if I type in CD downloads now , I am in the downloads folder .
Ok .
And how do I know ?
I'm in downloads folder .
P W D .
It actually tells you right here .
So I'm in home slash Saki slash downloads .
Ok .
And let's see what we have in downloads right now .
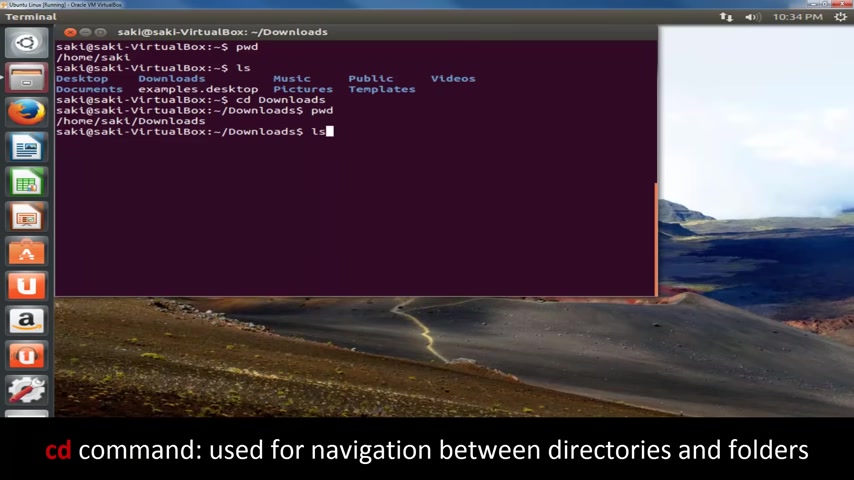
Type in list and there's nothing in downloads .
So let's , uh , launch this again .
Go to downloads .
And as you can see , downloads directory is actually empty .
Ok .
So if it is empty you're not going to see anything here .
Now , let's say I want to go back to my home directory , my soy directory .
How do I go back ?
So CD takes you into a folder and if you want to go out , what you do is you type in CD space two dots and that takes you back to the previous directory that you were focused on .
Now , if you want to go to the root directory , which is like um in , in windows , it's like the C directory , what you type is CD forward slash , make sure you put the space .
Ok ?
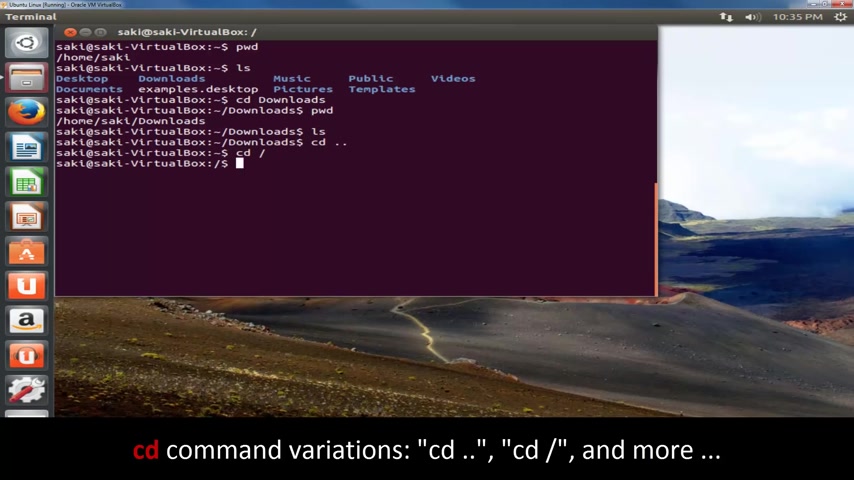
So CD , space forward slash press enter and that's gonna take you to the root directory .
Let's type in L S and as you can see the root directory has much more then your user directory .
Ok .
Again , but home and Saki is inside of root , root is at the top of everything .
So if you look around carefully , you'll see the home directory sitting in the root directory .
And if you go in there CD home and you type in L S , you will see your user name .
OK ?
And then CD Saki and then you type in L S and now you're back over here , this and this match .
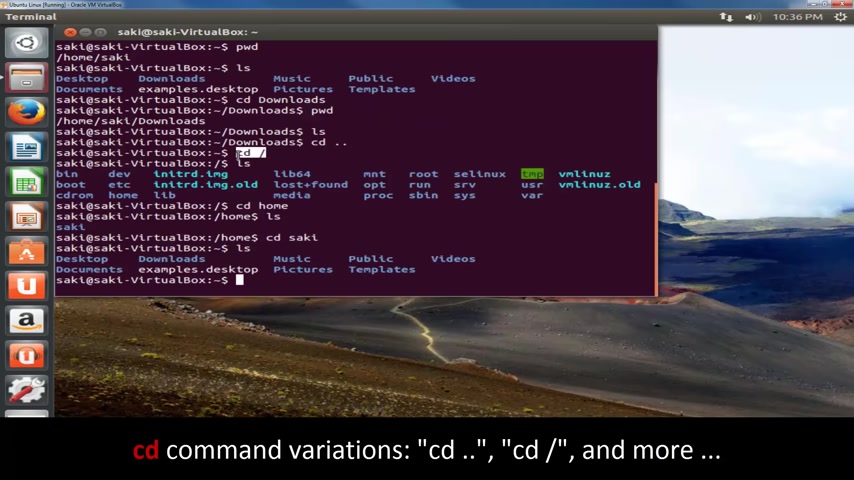
So remember this will take you to the root of your Linux operating system and inside of root , you've got all kinds of fancy things that you don't want to worry about right now .
So let's do a quick recap .
Let's go to the musics folder , CD , music .
So I'm now in the musics folder or the directory .
I'm going to be using the word folder and directory interchangeably interchangeably and they're going to be , be meaning the same exact thing .
Ok ?
So in here , let's type in P W D .
So that means print , print working directory and it tells you that you are in fact focused on the music folder .
Again .
If you go over here , here's the music folder .
If you go to home , here's the music folder .
Ok .
It's empty .
Let's type in L S to see if it is really empty .
It is in fact empty .

So next , I'm gonna show you how to copy or move a file .
So let's go back CD space dot dot takes us back and do an L S and let's say I want to go into the documents folder .
So I type in CD documents and then type in L S and here what I have is I have a test file .
So this is one of the files .
What I want to do .
What I want to do is I want to copy this file and I'm going to use the C P command for that .
That stands for a copy .
I'm gonna copy this test file and I'm going to paste it into the same folder with a different name .
So test copy and I'm going to press enter , OK ?
Just to give you , make you understand exactly what happens .
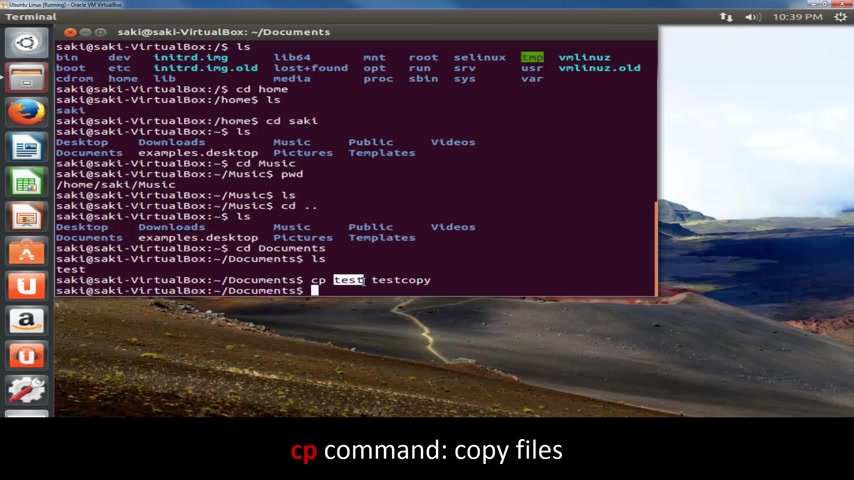
So you use the copy command , you pick the file that you're trying to copy and then you give it a brand new name to create the copy within the same folder .
OK ?
So if I type in L S now you have the first file test and then you've got test copy .
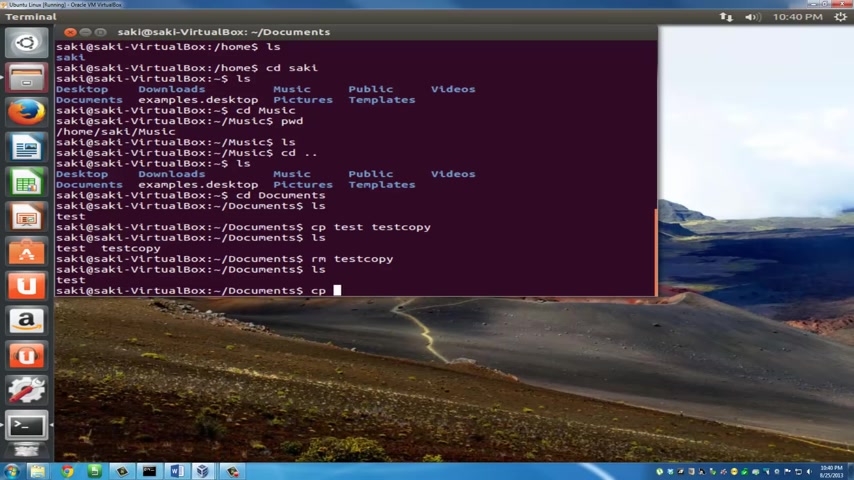
Now , how do I remove this file ?
You use the R M command .
OK ?
So the R M command is used to delete a file in your current folder .
So if you type in R M test copy and you type in L S , as you can see , test copy is gone and we only have test left over .
Now , what if I want to copy , test file ?
And I want to paste it into the downloads folder ?
How do you do that ?
OK .
What you got to do is you have to type in C P and you take the test file and then you have to tell the computer where do you want to put the copy of the test file .
So remember if you go up here , we're working under home slash Saki .
Ok .
So what you wanna do is you wanna do slash home slash slash downloads and you press enter and type in L S , we still have the test file right here .
Now , let's go back CD dot dot type in L S and let's navigate to the downloads folder .
And if I type in L S here , now we've got the , the file test sitting here which we copied over from the documents folder .
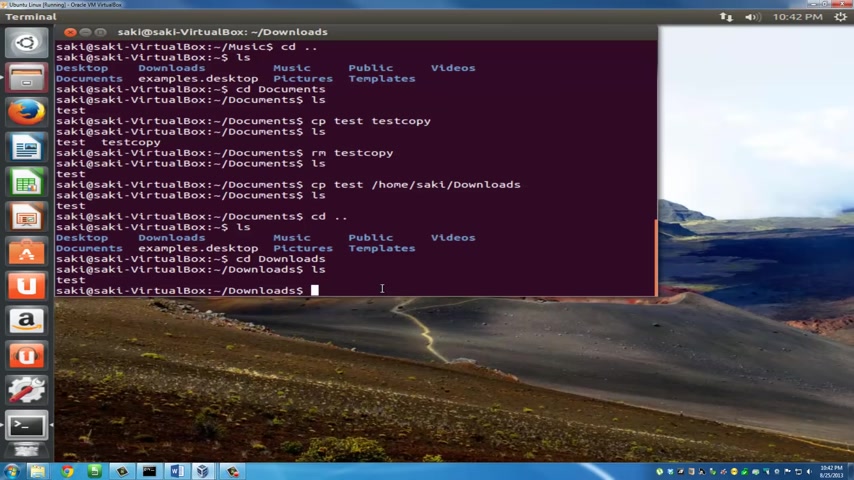
So let's go ahead and remove this file from the downloads folder .
So R M is the remove command R M test .
And remember because we are focused into downloads .
When we do R M test , it's gonna do , it's gonna delete the test file only from the downloads folder because that is where we are focused on press , enter type in list one more time L s and now there's nothing there left .
So let's go back , let's just type in P W D and we're back in home .
So next , next , let's talk about making a new folder and deleting the new folder .
So let me launch this right here and I'm going to minimize , I'm make this a little thinner here .
Ok ?
So you can still see what's going on one second .
All right .
So that's better .
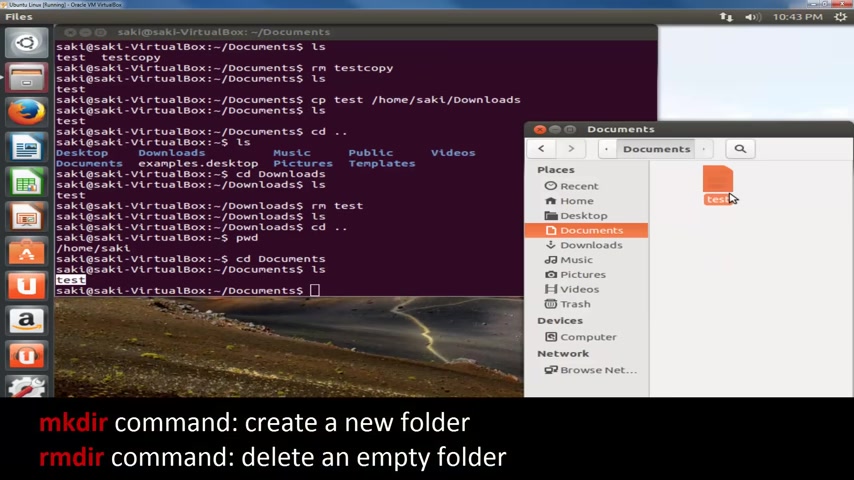
So let's go to my , um my documents over here and let's go to CD documents .
Oops , documents .
Ok .
So now we're in the documents folder and all we have in here is the test file which you can see right here .
Let's make a new folder .
So how do you make a new folder ?
You use the command called M K D I R press enter and it's gonna say some kind of error because we were missing an operant .
Ok ?
So we were missing the new directory .
We use the command but we did not specify the name of the directory .
So you type in M K D D I R and then you type in test folder .
I'm gonna use capital letters here .
Ok ?
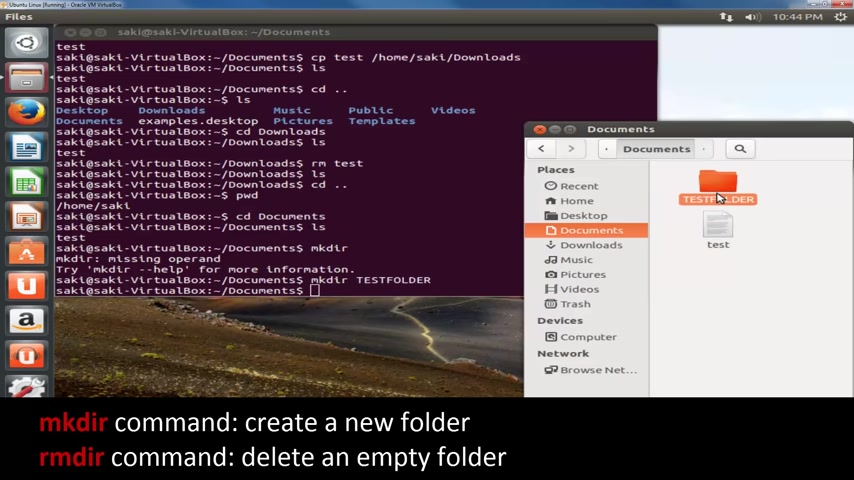
And as you can see over here , a test folder was created instantly and I can actually go into that test folder if I wanted to L S and there's nothing in there .
So let's go back CD dot dot And let's delete the test folder .
So how do you delete that ?
What you do is you use the , you use the command R MD I R .
So this one is make directory .
This one is remove directory type in test folder and I'm not going to press enter , take a look over here and let's come back here and press enter and that directory disappears .
Now , if the directory has something inside it , we cannot delete the directory that has stuff in it using R MD I R .
Ok .
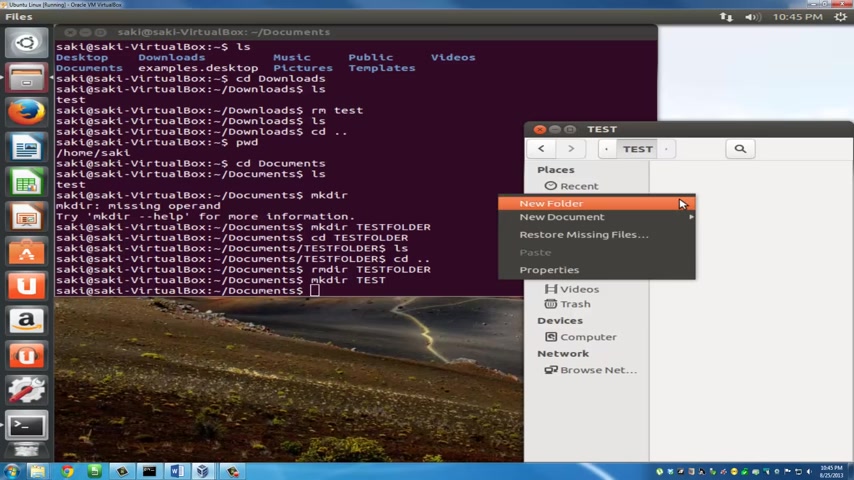
So let's uh M K D I R make another directory in the documents folder and say test .
OK .
So it popped up right here and let's go inside here and let's just create a new document .
Ok .
New doc .
Now , if I try to delete this using R MD I R test folder , let's go back here .
Ok .
So now the test folder has a file in it .
It is the new doc .
OK ?
If I try to delete this , it's gonna say failed to remove test directory is not empty .
So how do you delete this ?
You have to actually use the R M command , which is a remove command for files .
But what you do is you have to set a new option .
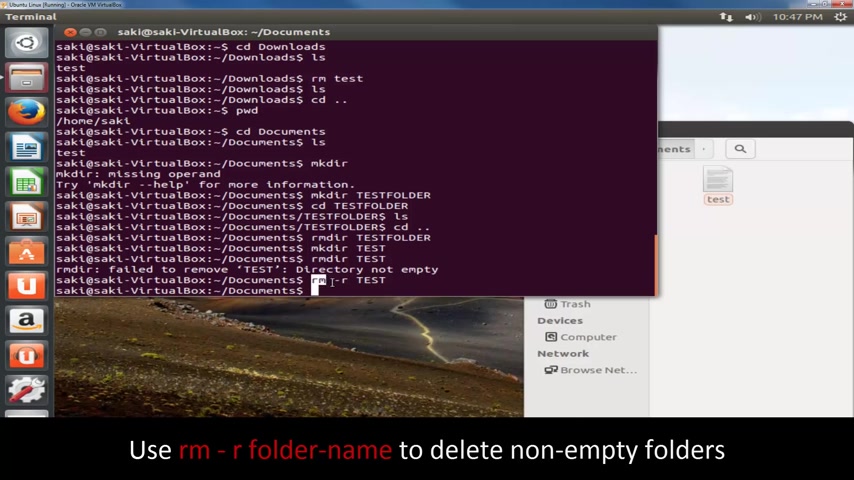
You have to say minus R and then you have to type in test .
OK ?
So watch this .
There's still a fall in here , but it's just going to disappear .
OK ?
So everything in test has been removed .
So this is how you delete folders that have existing files inside of them .
You use the R M command , you put a space , you put a minus R and then you put a space and then you put the name of the directory right underneath uh right next to minus R .
OK ?
So here it's gotten really messy here .
So let's use the clear command to clear the screen real quick .
And I'm gonna talk about a couple other commands and we're gonna , and the tutorial here .
All right .
So the final command I want to go over is called the man command .
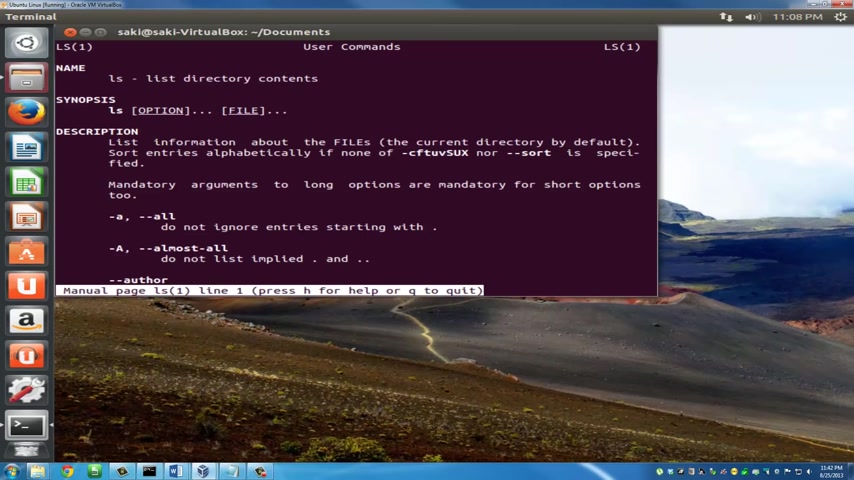
OK , ma N now this stands for manual manuals , OK ?
Like uh like tutorials .
So when you don't know what you're doing and you want to find out more about any command that you're using , you can type in man space and let's just say the L S command , which is the list command and you press enter , it's going to give you a whole lot of information regarding the L S command .
So you're going to get the name of the command , which is L S , it says list directory contents .
OK ?
You get a quick syna synopsis , you get a description of what the command exactly does and all that stuff .
And once you're done reading this whole thing , you just type key Q to quit .
OK ?
So let's do one more man .
And let's do the C P command , which is the copy command .
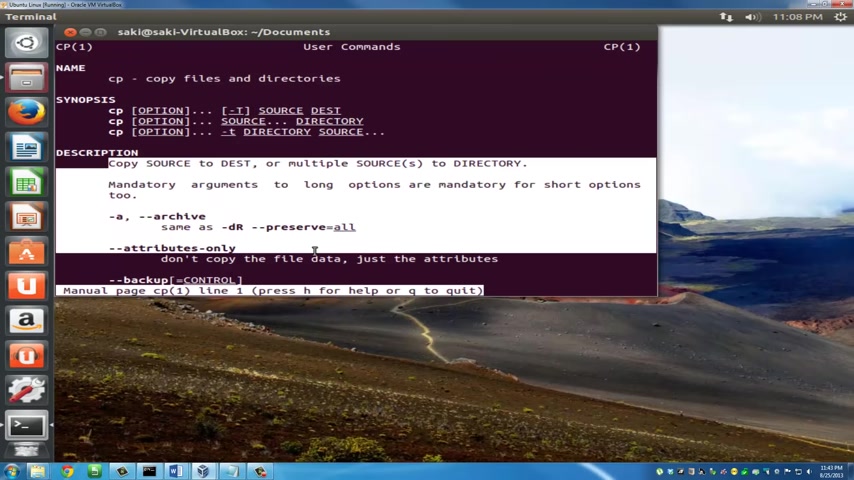
Press enter and it says here it copies files and directories .
OK ?
And you have a description here and you can read through this whole thing and you can keep pressing enter to get more information .
So press enter to continue .
OK ?
To go all the way .
But when you're done , you can press Q and it just quits the manual .
So that's how you can get information on any command that you want in Linux .
All right .
And thank you for watching this video .
Now , there are going to be more Linux tutorials coming soon .
So go ahead and subscribe to my channel for more videos to come .
Give me a thumbs up if you liked this video .
And you can also follow me on Facebook , Google Plus and Twitter .
Ok .
So we have all these options .
All links to my social media websites and my actual website are found in the description below .

All right .
Thanks for watching again and I'll see you the next time .
Are you looking for a way to reach a wider audience and get more views on your videos?
Our innovative video to text transcribing service can help you do just that.
We provide accurate transcriptions of your videos along with visual content that will help you attract new viewers and keep them engaged. Plus, our data analytics and ad campaign tools can help you monetize your content and maximize your revenue.
Let's partner up and take your video content to the next level!
Contact us today to learn more.